What the Heck is EOS? by Gino Wickman | Summary
Tom Bouwer and Gino Wickman coauthored What the Heck is EOS?: A Complete Guide for Employees in Companies Running on EOS, which provides a complete guide on the Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS) for employees. You, as the employee, play a crucial role in the success of your company.
This book is one of the best EOS books and provides EOS tools to help individuals get the EOS system used within their entire company to solve issues, plan and prioritize work, follow processes, communicate with one another, measure data, clarify roles, and lead and manage projects and people.
Buy What the Heck is EOS on Amazon

What the Heck is EOS?
A Complete Guide For Employees In Companies Running On EOS
This EOS management book is part of a larger series about the Entrepreneurial Operating System, which is a complete business model and interconnected tools to help leadership teams improve, gain traction, and grow their companies.
There are Six Key Components in EOS, which are Vision, People, Data, Issues, Process, and Traction. To learn more, Gino Wickman has detailed the EOS implementation checklist or process in his book, Traction, which we have summarized here.
What does EOS stand for? What does EOS mean in business? Thus, Gino Wickman and Tom Bouwer wrote What the Heck is EOS? to help your employees be more successful in a company using an EOS strategy.
Download the Book Summary for What the Heck is EOS?: A Complete Guide for Employees in Companies Running on EOS (pdf):
Gino Wickman is one of the co-founders of EOS Worldwide and is proud to say that “we run on EOS.” And Tom Bouwer is a Certified Professional EOS Implementer at EOS World Wide that helps growth-oriented companies simplify, clarify, and achieve their vision by implementing EOS.
Together, they are successful business leaders that show you what the Heck is EOS and how to succeed in just a few ways as an employee within your company.
Chapter 1 – What The Heck Is EOS?
Your company has an Operating System:
Business Operating System – the way that a company organizes its human capital, including how it holds meetings, solves issues, plans, and structures itself
If you are reading What the Heck is EOS, your company probably runs on the Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS), meaning:
Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS®) – the corporate structure that provides consistency of process to an organization and allows its employees to grow, to be fulfilled, and achieve their goals
This effective business system is designed for growth-oriented companies systematically that have 10 to 250 employees, are open-minded, and are growth-oriented. If you are starting out in entrepreneurship, check out Gino Wickman’s Entrepreneurial Leap (book summary).
Chapter 2 – The EOS Model: How Does EOS Work?
First in What the Heck is EOS?, Gino Wickman helps you understand the big picture of the EOS model:
EOS Model – every EOS company is comprised of the Six Key Components: Vision, People, Data, Issues, Process, and Traction
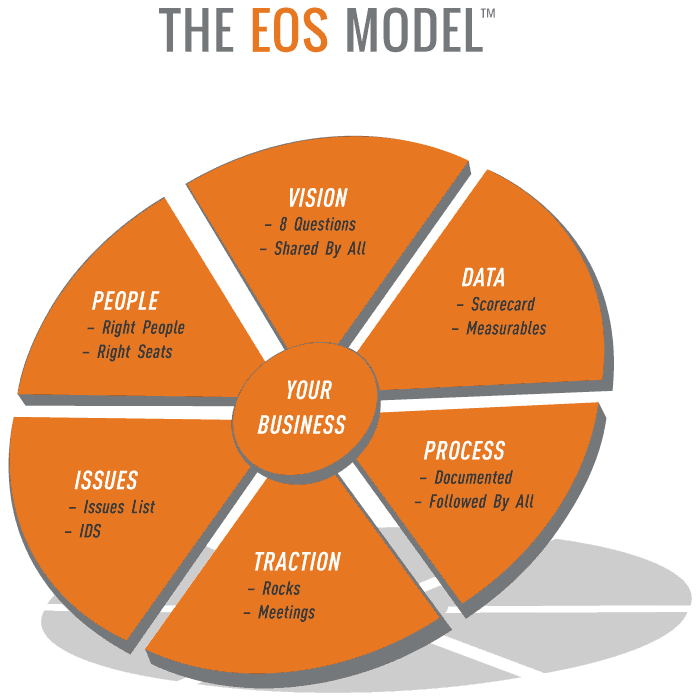
Six Key Components
When the Six Key Components are strong, then everyone in the organization will be moving in the same direction:
- Vision – component to get everyone aligned and focused on the same vision
- People – component to get the right people in the right seats
- Data – component to objectively measure performance and have a pulse
- Issues – component to identify, discuss, and solve issues
- Process – component to standardize and document the way that tasks are performed
- Traction – work toward achieving your rocks and actively participate in meetings
Your Role:
- Vision: Understand and trust in the vision laid out by the leadership and management team.
- People: Ask yourself if you are the Right Person in the Right Seat.
- Data: Establish and achieve your metrics.
- Issues: Raise problems to managers and help solve them.
- Process: Understand, follow, and improve the core processes.
- Traction: Achieve your Rocks and participate in meetings.
Ask Your Manager:
- What is our weakest component? How can I help improve it?
- What is our strongest component? Why do you think it’s the strongest?
- What is the first step you want me to take to help implement EOS in our organization?
Chapter 3 – The Vision/Traction Organizer (V/TO): Do You See What They Are Saying?

As an employee, Gino Wickman in What the Heck is EOS? states that youshould understand and believe in your company’s Vision, which is codified in the EOS V/TO or Vision/Traction Organizer:
Vision/Traction Organizer (V/TO) – an EOS tool to help your leadership team define, document, align upon, and disseminate the organization’s Vision
Eight Vision Questions
The leadership establishes the V/TO by answering the following eight questions:
- What are your Core Values? The Core Values define who you are as an organization within three to seven guiding principles. They codify behavior, define corporate culture, and the show uniqueness of the organization.
- What is your Core Focus? The Core Focus explains why your company exists and what you do in the world. Your why (Purpose, Cause, or Passion) is an overriding belief that empowers you to work. Your what is known as a Niche, which defines the domain in which you do business.
- What is your 10-Year Target? The 10-Year Target™ is the long-term, colossal goal for where your organization is going. It will improve how you focus efforts, allocate resources, and make decisions.
- What is your Marketing Strategy? The Marketing Strategy is the sales messaging that you are communicating with your potential customers. There are four elements for Marketing Strategy:
- Target Market, or the attributes of your ideal customers;
- Three Uniques, or the three characteristics that differentiate your company in your niche;
- Proven Process, or the consistent process of delivering your product or service to ensure customer satisfaction; and
- Guarantee, or the promise you make to your customers to ease them to buy.
- What is your 3-Year Picture? The 3-Year Picture™ is the mid-term goal for where the organization is going in the next three years. Derived from the 10-Year Target, it creates a vivid picture for three years, including revenue, profit, and measurables.
- What is your 1-Year Plan? The 1-Year Plan encompasses the three to seven company objectives for the next 12 months. Derived from the 3-Year Picture, it establishes the EOS annal planning agenda and yearly targets for revenue, profit, and measurables.
- What are your Rocks? Rocks are the company’s three to seven priorities for the next quarter. They break down yearly goals into smaller, manageable projects to maximize individual focus and energy.
- What are your Issues? Issues are the obstacles or mistakes that will prevent you from achieving your Vision. The V/TO Issues List stores your problems to help your company identify, prioritize, and solve them one at a time.
Your Role:
- Understand and believe in your company’s Vision, which is codified in the V/TO.
- Align all your efforts toward helping achieve that Vision.
Ask Your Manager:
- How can our department help achieve the organization’s Vision?
- How do I contribute to accomplishing the Vision?
- What is our greatest challenge in realizing our Vision?
Download the Book Summary for What the Heck is EOS?: A Complete Guide for Employees in Companies Running on EOS by Gino Wickman (pdf):
Chapter 4 – The Accountability Chart: Who’s Doing What?
Many companies have organizational charts, which show you who reports to who. However, these charts typically don’t help you figure out who is accountable for what. Instead, your company should use an Accountability Chart:
Accountability Chart – EOS organizational chart or traction org chart that illustrates the right structure, which will:
- Clarify roles and responsibilities so that accountability is clear.
- Create clear reporting lines so an employee reports to one boss.
- Facilitate efficient decision-making and problem-solving.
- Help people know who to work with to get things done.
- Enable communication flow.
- Identify all of the available seats in the organization.
- For each seat, show the five or so major roles for that job.
For more on leadership, check out The 5 Levels of Leadership (book summary).
Your Role:
- Know where you fit in your company’s Accountability Chart.
- Understand and fulfill the responsibilities of your role.
- Ask yourself if you are the Right Person in the Right Seat
Ask Your Manager:
- What seat am I in, and what are my 5 roles and responsibilities?
- Am I in the Right Seat where I can contribute the most to the organization?
- What are your 5 roles and/or responsibilities, and how can I help you?
Chapter 5 – Rocks: What is Most Important Right Now?

Every quarter, Gino Wickman says in What the Heck is EOS? that you should establish one to three Rocks through discussions with your manager and team. This is the EOS Rocks definition:
Rocks – the most important goals or priorities that must get done in the next 90 days
- For the company and leadership team: about three to seven Rocks aligned with the company’s Rocks
- For employees: about one to three Rocks aligned with your manager or company’s Rocks
After the Rocks have been set for the team, they should be entered onto the EOS Rock Sheet. The Rock Sheet is a piece of paper that lists team Rocks followed by individual Rocks. Then, during weekly meetings, the EOS Rocks Sheet is reviewed to ensure that all Rocks are tracking to the 90-day World:
90-Day World – quarterly time interval in which to set Rocks for the company and its employees
Rocks are set every 90 days due to human nature. After 90 days of working on projects, the human mind tends to lose focus and become distracted. For more help writing great Rocks or to get EOS rocks explained, check out this EOS Rocks video. Further, to create a 90-day plan, check out The 12 Week Year (book summary).
SMART Rocks
You should establish your Rocks using the SMART framework:
- S – Simple: Do you know what you need to do to get started to work on the Rock?
- M – Meaningful: Do you have a quick understanding of the importance of completing that Rock?
- A – Actionable: Do you know what 10X actions you need to take to accomplish the Rock?
- R – Realistic: Can you achieve the Rock in 90 days with the resources you have available?
- T – Trackable: Can you quantitatively measure the progress toward completing the Rock?
Your Role:
- Establish one to three quarterly Rocks through discussions with your manager and team.
- Work to complete your Rocks using the SMART framework.
Ask Your Manager:
- When will we start establishing Rocks (if not doing so already)?
- Do you think my Rocks are appropriate for me?
- What are your Rocks?
- How can I help you achieve them?
Chapter 6 – The Weekly Meeting Pulse: Why Do We Have To Have Meetings?

Most of the time, humans procrastinate, so in What the Heck is EOS?, Gino Wickman suggests harnessing this procrastination on a regular basis using the Weekly Meeting Pulse:
Weekly Meeting Pulse – the EOS process of holding consistent meetings, which causes increases in work produced, improves communication, and holds people accountable within an organization
You should participate and raise issues in your team’s Level 10 Meeting:
Level 10 Meeting (L10) – the 90-minute meeting for your leadership and departmental teams that your employees rate a “10” (scale from 1 to 10) for productivity and effectiveness; key attributes include:
- Keep you focused on what is essential and help you resolve issues;
- Should be held at the same time and day each week;
- Follow the same meeting agenda, and
- Start and end on time.
- Follow the three-step Issues Solving Track: Identify, Discuss, and Solve.
Two roles are crucial for running team meetings:
- Meeting Facilitator – the person responsible for running the meeting and keeping everyone working on schedule and time
- Document Manager – the person responsible for updating the meeting agenda, datasheet, and priorities, and Rocks
Level 10 Meeting Agenda
The Level 10 Meeting format follows this agenda:
- Introduction: Start the meeting on time.
- Segue (Share Good News): Transition from work mode, in which team members can share positive news, either professional or personal.
- Scorecard (Datasheet): Review each of the team’s Measurables or metrics to be accountable to whether they are tracking for a specific objective.
- Rocks (Objectives): Review each team member’s Rocks to be accountable to whether they are tracking to accomplish them.
- Customer or Employee News: Provides time for anyone to share important news regarding work, employees, or customers.
- To-dos (Tasks): Review each to-do or weekly action item to confirm that it was done in the past week.
- Solve Issues: Review the Issues List (see below) and use the Issues Solving Track to solve your team’s three major problems.
- Conclusion: Recap the significant parts of the meeting, including public announcements and action items. End the session on time, tie up loose ends, and rate the meeting.
In your meeting, your team should be open to discussing problems and review the Issues List:
Issues List – the catalog for the problems in your team or company in which decisions have to be made, information has to be shared, or information is required to take action
Then, you should use the Issues Solving Track to resolve your most significant issues:
Issues Solving Track – a framework to solve issues using the following EOS processes:
- Identify major weekly problems and underlying causes.
- Discuss the solution to those issues.
- Solve the problems and assign someone to be responsible.
Your Role:
- Participate and bring up problems in your team’s Level 10 Meeting.
- Allow for free speech and openness when discussing issues in your team’s Level 10 Meeting.
- Fight for the best interest of your team and organization.
- Hold yourself and the team accountable on Rocks, measurables, and tasks.
Ask Your Manager:
- Will I be punished for bringing up any issues in the Level 10 Meeting?
- Will you get upset if I grade the meeting with a low score?
- How can we improve our Level 10 Meeting?
Download the Book Summary for What the Heck is EOS?: A Complete Guide for Employees in Companies Running on EOS (pdf):
Chapter 7 – Scorecard & Measurables: What’s My Number?

Each week in your Level 10 Meeting, you and your team will review the department’s weekly Scorecard:
Scorecard – datasheet containing the metrics or data to show how the organization (5-15 metrics) or department (3-5 metrics) is performing, identify and solve issues, and remove subjectivity from communication; it should include the following:
- Who – the person responsible for each of the metrics
- Measurables – the 3 to 5 metrics that are recorded on the weekly Scorecard
- Goal – the target number that must be reached every week
- Date – the week that you are reporting on
Your department can use the IDS framework to resolve any numbers that are not on track. Also, you can check out an EOS Scorecard template and examples here.
Lastly, you should know your specific Measurables and constantly work to achieve them:
Measurable – a metric or data point that is being tracked for an employee, department, or company; preferably be activity-based leading indicators
Your Roles:
- Review your department’s Scorecard each week in your Level 10 Meeting.
- Help to resolve any numbers that are not on track using the IDS framework.
- Know your specific Measurables or metrics and constantly hit them.
Ask Your Manager:
- Does our departmental Scorecard contain the right metrics and objectives?
- From these suggestions, which one is a good Measurable or metric for me?
- What are your Measurables or metrics? How do I help you hit them?
Chapter 8 – People Analyzer: How Am I Doing?

In What the Heck.is EOS?, Gino Wickman recommends evaluating yourself honestly as an employee, using the People Analyzer:
People Analyzer – an entrepreneurship operating system tool that gets the Right People in the Right Seats in your organization using a few inexpensive steps:
Step 1. Right People
Evaluate if you, the candidate, embody your organization’s Core Values using the EOS Rating System:
EOS Rating System – want a minimum threshold of three +’s and two +/-’s for the Core Values:
- Plus (+): Candidate mostly embodies the Core Value
- Plus/Minus (+/−): Candidate sometimes embodies the Core Value
- Minus (−): Candidate rarely embodies the Core Value
Step 2. Right Seat
Determine if you, the candidate, fit into the roles and responsibilities of your seat using the GWC tool:
Get It, Want It, and Capacity To Do It (GWC):
- Get It: Do you, the candidate, understand the position and how it fits within the organization?
- Want It: Do you, the candidate, have a genuine desire and passion for the position?
- Capacity To Do It: Do you, the candidate, have the emotional, intellectual, physical, and timely ability for the position?
If you are wondering how your manager views your performance, then you should meet with your manager for your Quarterly Conversation:
Quarterly Conversation – informal, face-to-face, one-on-one 60-minute meeting between you and your boss to discuss projects, clarify expectations, communicate well, and resolve issues, if necessary
Your Role:
- Evaluate yourself honestly, using the People Analyzer.
- Meet with your manager to have your Quarterly Conversation.
Ask Your Manager:
- What was your analysis of me, using the People Analyzer?
- When will we start having Quarterly Conversations?
- What do you think is working, and what is not working?
Chapter 9 – Organizational Checkup: What Do I Do Next?
Lastly, to figure out whether your organization is successful on EOS, conduct an Organizational Checkup:
Organizational Checkup – an EOS tool consisting of 20 questions to determine the current state of your company
Download the Book Summary for What the Heck is EOS?: A Complete Guide for Employees in Companies Running on EOS by Gino Wickman (pdf):
Next Steps
EOS Worldwide reviews show that great employees allow entrepreneurs to grow and scale their companies. I hope this post will help you be more successful within your organization using the EOS Model. Also, I hope you are inspired to get your own copy of What the Heck is EOS or check out the rest of the EOS books:
- Traction (book summary): Helps company owners implement EOS and the Six Key Components to gain traction and grow their successful businesses.
- Get a Grip (book summary): Tells a fictional business fable about an entrepreneurial company hitting the ceiling. In response, the company’s leadership implements EOS for success.
- Rocket Fuel (book summary): Provides a guide for the integral relationship between a Visionary and an Integrator.
- How to Be a Great Boss (book summary): Helps leaders and managers at all levels of an organization use timeless business principles to get the most from their people.
- The EOS Life (pdf book summary): How to live your ideal entrepreneurial life “doing what you love, with people you love, making a huge difference, being compensated appropriately, with time for other passions.”
- Process (book summary): Helps you document, simply, and package your core processes such that they are followed by all in your organization.
For more, check out the EOS blog here or EOS Worldwide Conference here.